Total Risk= Unique Risk + Market Risk
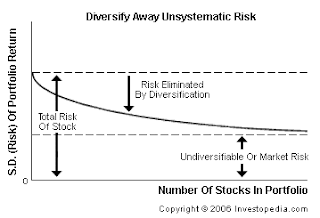
The unique risk of a security represents that portion of its total risk which stems from firm specific factors like the development of anew product , a labor strike, or the emergence of a new competitor. Events of this nature primarily affect the specific firm and not all firms in general. Hence the unique risk of a stock can be washed away by combining it with other stocks. In diversified portfolio, unique risks of different stocks tend to cancel each other- a favorable development in one firm may offset an adverse happening in another and vice versa. Hence, unique risk is also referred to as diversifiable risk or unsystematic risk.
The market risk of a stock represents that portion of its risk which is attributable to economy wide factors like growth rate of GNP, the level of government spending, money supply, interest rate structure and inflation rate. Since these factors affect all firms to a greater or lesser degree, investors cannot avoid the risk arising from them, how ever diversified their portfolios may be. Hence , it is also referred to as systematic risk( as it affects all securities) or non-diversifiable risk.

Comments
Post a Comment