The randomness of stock prices was the result of an efficient market. The key links in the argument are as follows:
- Information is freely and instantaneously available to all the market participants
- Keen competition among market participants more or less ensures that market prices will reflect intrinsic values. This means that they will fully impound all available information.
- Prices change in response to new information that by definition is unrelated to previous information otherwise it will not be new information.
- Since new information cannot be predicted in advance, price changes too cannot be forecast .Hence prices behave like a random walk.
What is an Efficient Market?
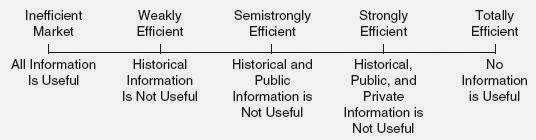
An efficient market is one in which the market price of a security is an unbiased estimate of its intrinsic value.Market efficiency is defined in relation to information that is reflected in security prices. Eugene Fama suggested that it is useful to distinguish three levels of market efficiency:
- Weak Form Efficiency: Stock Prices reflect all information found in the record of past prices and volumes.
- Semi Strong Efficiency: Stock Prices reflect not only all information found in the record of past prices and volumes but also all other publicly available information
- Strong Form Efficiency: Stock Prices reflect all available information,public as well as private
Comments
Post a Comment